Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus)
|
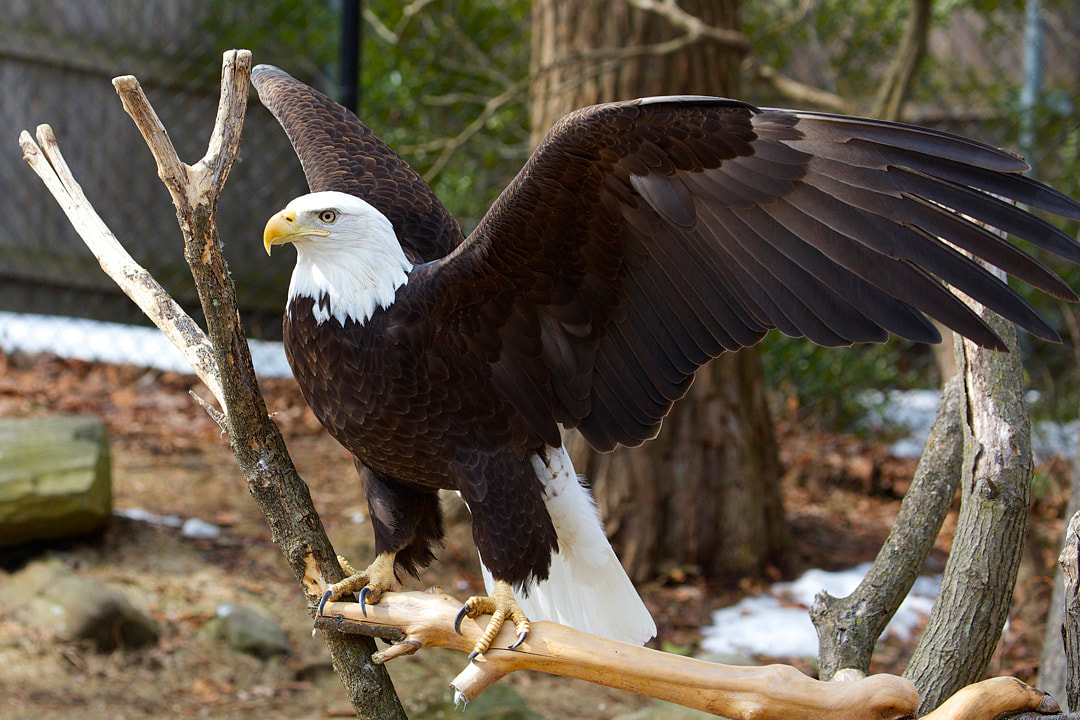
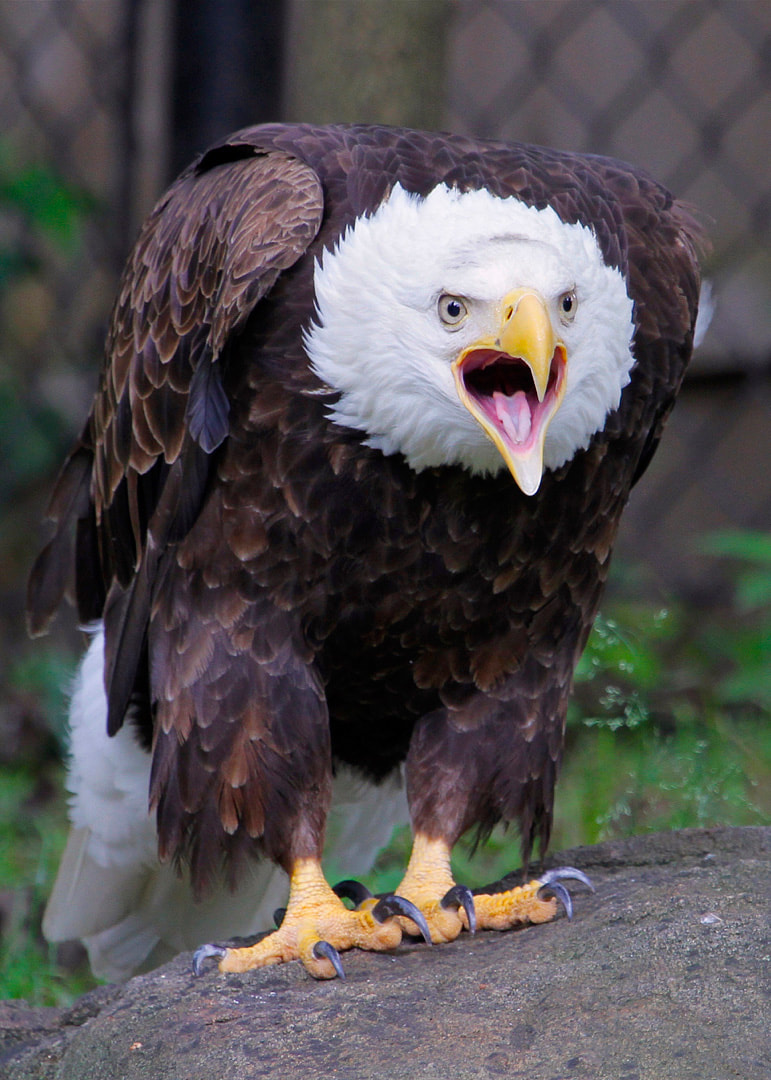
Physical Description: The Bald Eagle weighs 6.5 – 14 lbs and can have a wingspan up to 8 feet1. They have brown feathers across their body with white head, neck, and tail feathers as well as yellow feet and beak. Young Bald Eagles are a mix of white and brown across their body, and do not achieve their full brown plumage until 4-5 years of age.
Habitat: They Bald Eagle can inhabit a variety of ecosystems; however, they are typically found close to bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, streams, and ponds. Range: The Bald Eagle can be found across North America, with large populations centralized in Canada and the northern United States. Diet: The Bald Eagle is a carnivore who will eat a mix of live prey as well as carrion it scavenges and steals from other animals. Life Span: They live 15-30 years in the wild, and up to 50 years in human care2. Social Structure: Bald Eagles mate for life and build enormous nests for the pair of eggs they will lay each year. Females lay 1-3 eggs, which are incubated by both the male and the female for 35 days. Hatchlings remain in the nest for up to 20 weeks. Eagles reach maturity at 4-5 years of age at which time they obtain their white head feathers. Status: Least Concern3 References: 1 https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/bald-eagle 2 https://denverzoo.org/animals/bald-eagle/ 3 https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22695144/93492523 |
Other: The Bald Eagle, the national symbol of the United States, was almost wiped out entirely throughout the country. Hunting and DDT poisoning threatened the species, and it was not until strict pesticide guidelines were enforced and it became illegal to hunt this bird that the Bald Eagle population began to increase.
|