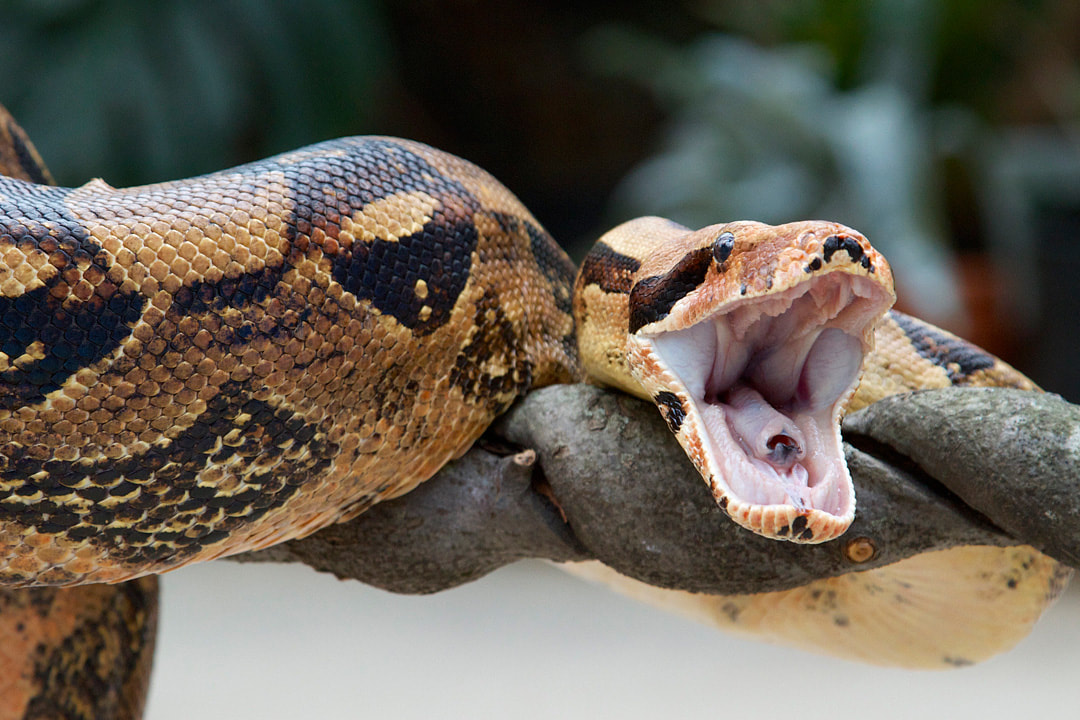
Boa Constrictor (Boa constrictor)
|
Physical Description: Cryptic, broken patterns of brown and cream resembling leaf litter adorn their bodies making them master of camouflage. Their length varies depending on where they reside. On Hog Island, off Central America, Boas seldom grow longer than 3 feet. In most of Central America, Boas reach 10 feet, and in Trinidad and Venezuela, they can grow to 20 feet.
Habitat: They primarily live in the rainforest but can also be found in semi-arid savannas. Range: They live in northern South America, in Venezuela, Colombia and Brazil, as well as along the southern edges of Central America. Diet: They are fierce carnivores, wrapping around their prey to catch it. Young boas dine on mice, small birds, lizards and frogs. Adults will eat monkeys, capybaras, agoutis, acouchis, caimans, and wild pigs. Lifespan: Boa constrictors live 20-30 years on average. Social Structure: They are solitary except during mating season. They are a ovoviviparous species. Females retain eggs in their bodies and give birth to 20 to 60 live young, measuring 17 to 20 inches each. Status: Least Concern1 Other: Although protected throughout most of its range, many skins are still sold to the leather trade each year. Numbers are also dropping due to habitat destruction. 1 https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/197462/2486405 |
Rainforest Building open daily from 10:30 am to 3:30 pm