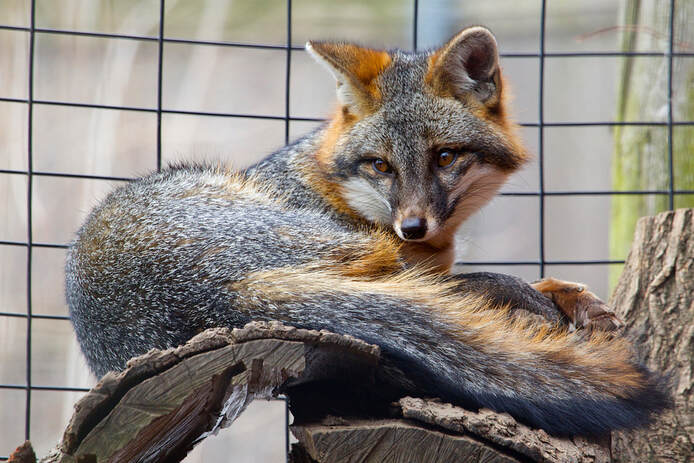
Gray Fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus)

Physical Description: The Grey Fox is named for its peppery gray fur along its back and head. The fur on their sides and legs is a reddish-brown color. They have a long bushy tail with a black stripe down the center. They have large, pointed ears, a pointed muzzle, and long hooked, retractable claws. Grey Foxes are 21 to 30 inches long but their tail can add up to 16 more inches. They weigh between 8 and 15 pounds.
They can climb well and sometimes climb to rest safely in a tree. They make their dens in hollow logs, caves, or crevices.
Habitat: They prefer woodlands and areas with lots of brush.
Range: The Grey Fox can be found as far north as Ontario, Canada and as far south as Venezuela. They like forests and densely vegetated areas, so they will not be found on the central plains of North America or in the Rocky Mountains.
Diet: They are omnivores. They eat small mammals like rabbits and mice, which make up the main part of the fox’s diet, but they also eat birds, insects, grasshoppers, fruits and berries.
Lifespan: They live 8 years in the wild and up to 12 years in human care.
Social Structure: Grey Foxes are monogamous. The female gives birth to 3 to 4 pups in the Spring. The pups are weaned by the age of three months and can hunt on their own at around four months. The male also helps to feed the pups. They leave their mother and their den in the Fall.
Status: Least Concern1
Other: They have long, hooked claws to grasp the tree trunk and scramble up and they can even move between branches.
Although they prefer to hunt at night Grey Foxes can be seen about any time of day so they are considered crepuscular animals.
The Grey Fox has a similar voice to a Red Fox but it is louder and less vocal.
1 https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22780/46178068
They can climb well and sometimes climb to rest safely in a tree. They make their dens in hollow logs, caves, or crevices.
Habitat: They prefer woodlands and areas with lots of brush.
Range: The Grey Fox can be found as far north as Ontario, Canada and as far south as Venezuela. They like forests and densely vegetated areas, so they will not be found on the central plains of North America or in the Rocky Mountains.
Diet: They are omnivores. They eat small mammals like rabbits and mice, which make up the main part of the fox’s diet, but they also eat birds, insects, grasshoppers, fruits and berries.
Lifespan: They live 8 years in the wild and up to 12 years in human care.
Social Structure: Grey Foxes are monogamous. The female gives birth to 3 to 4 pups in the Spring. The pups are weaned by the age of three months and can hunt on their own at around four months. The male also helps to feed the pups. They leave their mother and their den in the Fall.
Status: Least Concern1
Other: They have long, hooked claws to grasp the tree trunk and scramble up and they can even move between branches.
Although they prefer to hunt at night Grey Foxes can be seen about any time of day so they are considered crepuscular animals.
The Grey Fox has a similar voice to a Red Fox but it is louder and less vocal.
1 https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22780/46178068